Smart Assertions (AI Anomaly Detection) ⚡
What are Smart Assertions?
Smart Assertions are Anomaly Detection monitors that will train on the historical patterns of the data, and make predictions of what 'normal' looks like. They are powered by an incredibly sophisticated ML pipeline, enabling them to account for a large variety of trends in the data, including seasonality.
How do I create Smart Assertions?
Today, you can create Smart Assertions for 4 types of assertions. To learn more about each one, click the respective links below:
You can also create Freshness & Volume Smart Assertions in bulk on the Data Health page:
Improving Smart assertion quality
You can improve predictions through two key levers:
- Tuning
- Anomaly feedback
Tuning
You can fix most Smart Assertions with 3 key actions - correct training data, adjust sensitivity, and increasing the lookback window. Each of these can be accessed via the Tune Predictions button on the Assertion Profile, or the Settings tab.
Exclusion Windows Set time windows to exclude from training data. This can be useful to exclude known maintenance windows or other periods of downtime, seasonal spikes e.g. holidays or any other windows that are not representative of normal data trends.
Sensitivity A higher sensitivity will have a tighter fit on the data. A lower sensitivity will allow for more data variation before an anomaly is flagged.
Training data lookback window This is the number of days our ML models will look back to gather training data to generate predictions. If this is too large, we may pick up on old data that is no longer part of the current trend. If it is too short, we may miss key seasonal patterns. You can leverage this alongside exclusion windows to improve the quality of predictions.
Anomaly Feedback
False alarms
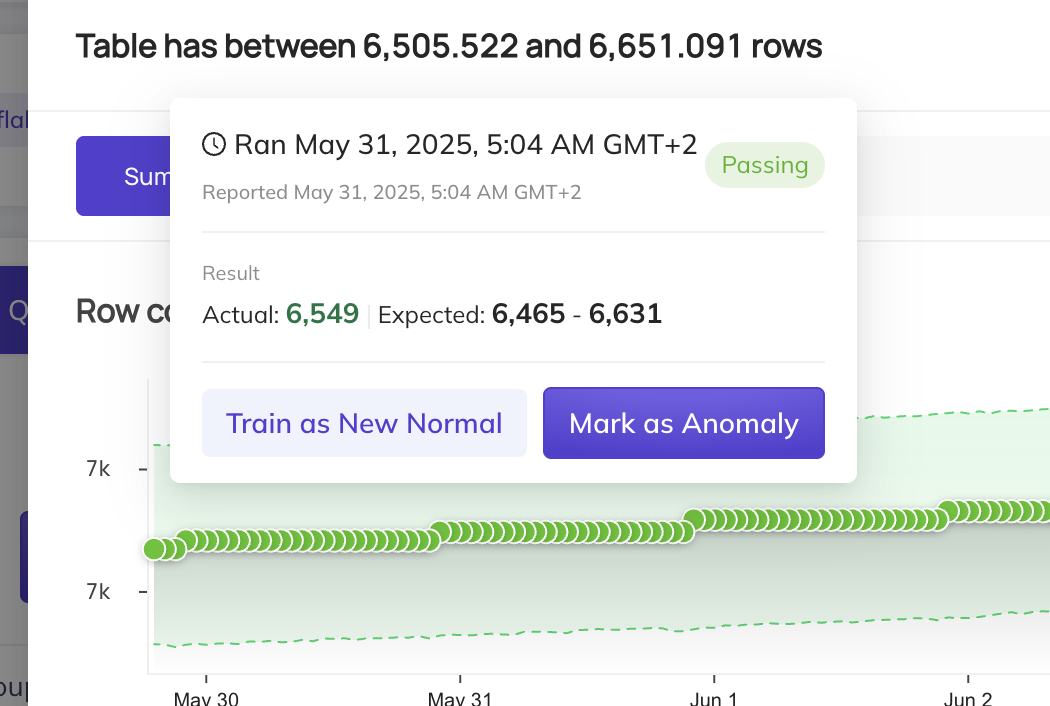
When an anomaly is flagged by the smart assertion, you may hover over the result dot and select Mark as Normal. This will include this data point in the training set, and the model will adjust to ensure it does not flag such data points as anomalies again.
However, there are some cases where anomalies are actually expected. For instance, if this is a sudden jump in data, but it will be the new normal moving forward, we recommend selecting the Train as new Normal option. This will add an exclusion window to all data prior to this run event, and the smart assertion will begin training on data points from this point forward.
Missed alarms
If an anomaly is not caught by our Smart Assertions, we recommend doing a few things:
- You can click
Mark as Anomalyto flag this specific data point as an anomaly. This will exclude that data point from the training data. - Click Tune Predictions on the assertion, then exclude any “bad” historical periods from the training set (by adding an
Exclusion Window). This is useful if older incidents or one-off events are polluting the model’s notion of “normal”. - Finally, consider increasing the sensitivity of the assertion in the Settings tab which will reduce the range of allowable values.