Logical Models
Currently we only support datasets and by extension schema fields for logical models. No other entity types are supported.
What is a Logical Model
A logical model represents the concept and structure of a database table, without being tied to any single physical instantiation in some source system. Like any DataHub dataset entity, a logical model describes its columns, including data types and descriptions, and can be attributed with other metadata like tags, terms, owners, and custom properties. But unlike physical datasets, logical models do not represent a table in a source system that actually exists, in which data is stored and can be queried.
Logical models are useful for those who have multiple tables that represent the same type or shap of data, or store the same data. This is common for multi-cloud data ecosystems, in which the same table may be replicated across several cloud providers, e.g. Snowflake, Redshift, and BigQuery. It is also useful in cases where multiple replicas exist in a single system, such as gold/silver/bronze layers. Logical models should be linked to each physical representation to expose this relationship DataHub. DataHub Cloud customers can take advantage further with Centralized Management, in which every physical child's metadata can be managed at the logical model level.
How It Looks
The environment variable LOGICAL_MODELS_ENABLED must be set to true on datahub-gms for logical models to be viewed in the UI.
For example, suppose there exists a Users table Snowflake, an AllUsers table in BigQuery, and a UsersAttributes table Apache Hive. These three tables may have different names and slightly different structures, but logically represent the same data: a table of users, with certain information (columns) for each user. We create a logical table called Users and link it to each physical child:
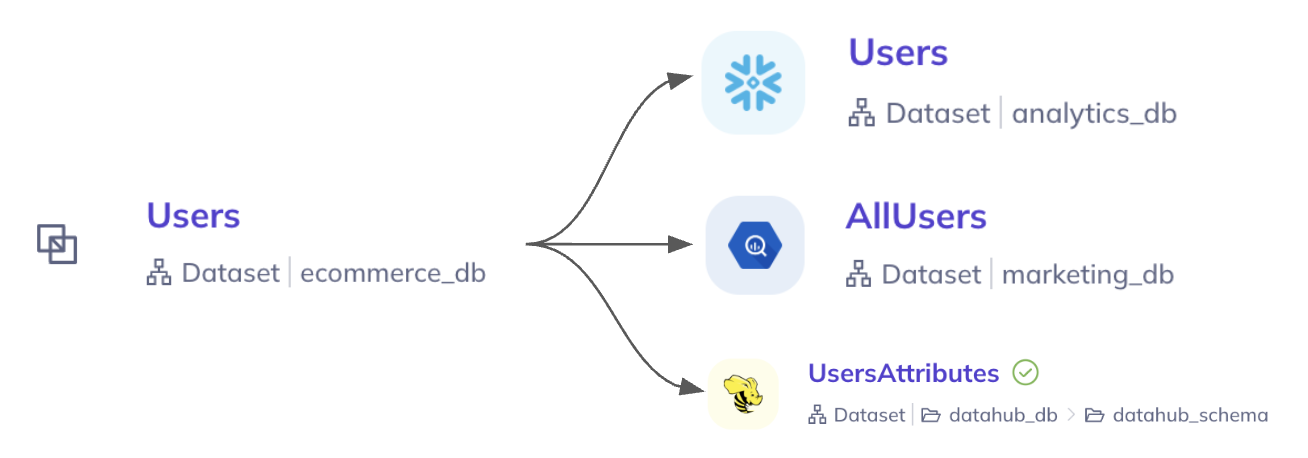
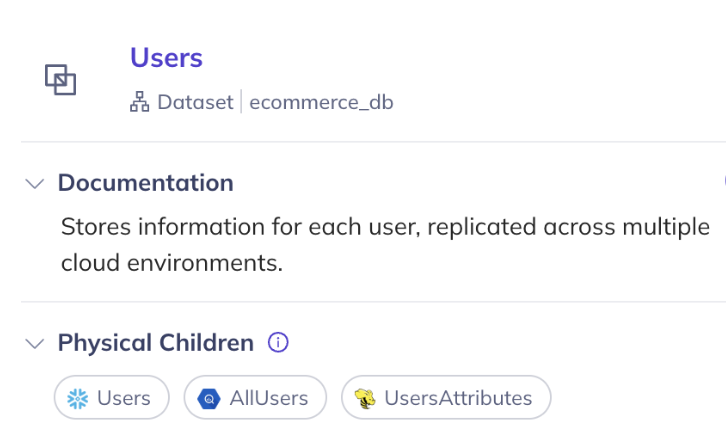
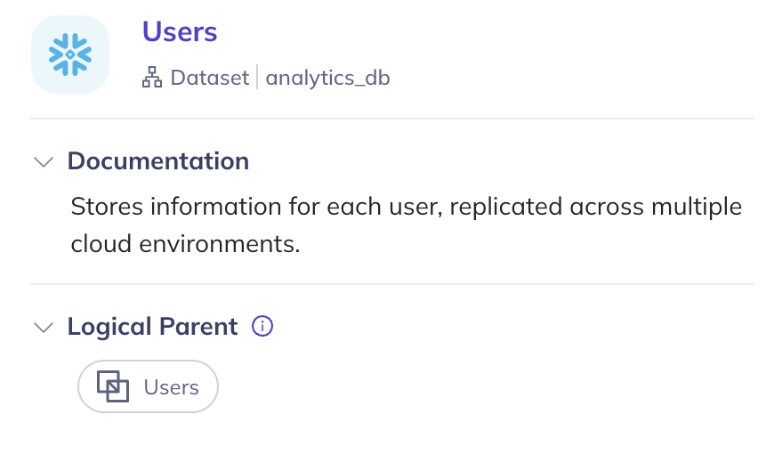
Once the relationships are created, they will show up in the entity sidebar for both logical parents and their physical children:
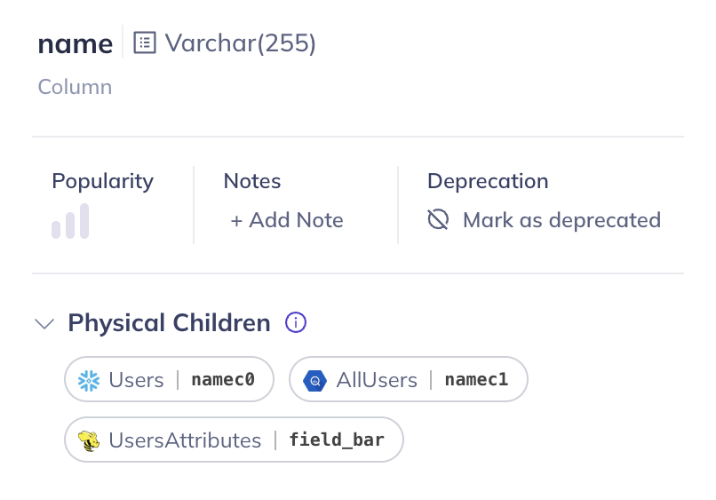
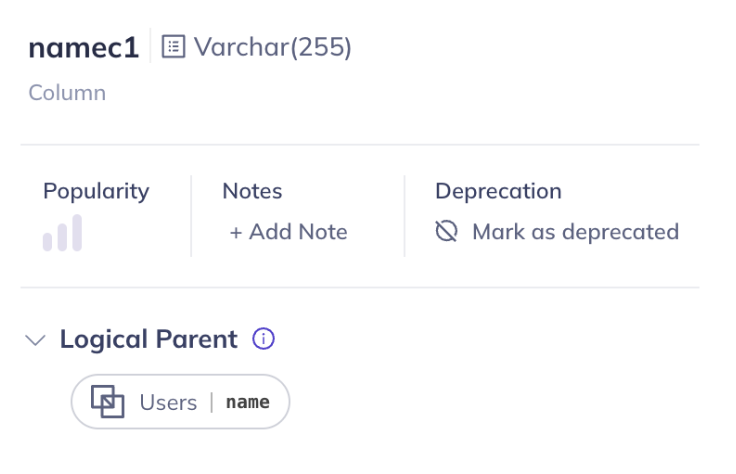
Columns on the logical parent and physical children can be linked as well:
Creating Logical Models
Logical models are created like any DataHub dataset. We recommend using the Python SDK.
All DataHub datasets require a platform, representing where the dataset exists. If your logical models are stored in a system users are familiar with, we recommend creating a custom platform for that system and providing a custom icon. Otherwise, we recommend using the platform logical, which has a special default icon.
Create Dataset in "logical" Platform
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient, Dataset
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
dataset = Dataset(
platform="logical",
name=logical_model_name,
description=logical_model_description,
schema=[
# tuples of (field name / field path, data type, description)
(
"zipcode",
"varchar(50)",
"This is the zipcode of the address. Specified using extended form and limited to addresses in the United States",
),
("street", "varchar(100)", "Street corresponding to the address"),
("date_column", "date", "Date of the last sale date for this property"),
],
)
client.entities.upsert(dataset)
Create Dataset in Custom Platform
# Create custom platform with custom logo
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import DataPlatformInfoClass, PlatformTypeClass
from datahub.metadata.urns import DataPlatformUrn
urn = DataPlatformUrn("<platformName>").urn()
aspect = DataPlatformInfoClass(
name="<platformName>",
type=PlatformTypeClass.OTHERS,
datasetNameDelimiter=".",
logoUrl="<url>"
)
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
client._graph.emit(MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(entityUrn=urn, aspect=aspect))
# Create dataset in custom platform
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient, Dataset
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
dataset = Dataset(
platform="<platformName>",
... # See above
)
client.entities.upsert(dataset)
Linking Logical Models
At its core, the logical -> physical relationship is created by the LogicalParent aspect. To link columns, this aspect must also be created on each child schmea field entity. However, for ease of use, we recommend the OpenAPI endpoint.
OpenAPI
The OpenAPI endpoint creates a logical -> physical relationship for a single logical-physical pair, as well as the column-level relationships between their columns, if specified.
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:8080/openapi/v3/logical/<physical_child_urn>/relationship/physicalInstanceOf/<logical_model_urn>' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"<logical_column_name_0>": "<physical_column_name_0>",
"<logical_column_name_1>": "<physical_column_name_1>",
"<logical_column_name_2>": "<physical_column_name_2>"
}'
These relationships can also be removed (as of DataHub Cloud v0.3.15):
curl -X DELETE 'http://localhost:8080/openapi/v3/logical/<physical_child_urn>/relationship/physicalInstanceOf' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
Python SDK
The Python SDK can also query the same endpoint:
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
url = f"{client._graph.config.server}/openapi/v3/logical/{child_urn}/relationship/physicalInstanceOf/{parent_urn}"
client._graph._post_generic(url, {column.parent_name: column.child_name for column in columns})
Or it can create a single relationship by emitting the LogicalParent aspect.
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import EdgeClass, LogicalParentClass
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
client._graph.emit(MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(entityUrn=child_urn, aspect=LogicalParentClass(parent=EdgeClass(destinationUrn=parent_urn))))
The relationship can also be removed:
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import EdgeClass, LogicalParentClass
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
client._graph.emit(MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(entityUrn=child_urn, aspect=LogicalParentClass(parent=None)))