Service Accounts
Available starting in DataHub Cloud v0.3.17, DataHub Core v1.4.0.
Introduction
Service Accounts provide a secure way to enable programmatic access to DataHub APIs without using personal user credentials. They are designed for automated workflows, CI/CD pipelines, data ingestion processes, and any other use case where a non-human identity needs to interact with DataHub.
Key benefits of using service accounts:
- Separation of Concerns - Decouple automation credentials from personal user accounts
- Auditable Access - Track API usage by specific automation workflows
- Granular Permissions - Assign specific roles and policies to each service account
- Token Management - Generate, rotate, and revoke tokens independently for each service account
- Security - Revoke access instantly without affecting human users
Prerequisites and Permissions
To manage service accounts, a user must have the Manage Service Accounts platform privilege. This privilege allows users to:
- Create new service accounts
- View and list existing service accounts
- Delete service accounts
- Generate access tokens for service accounts
By default, users with the Admin role have this privilege. You can grant this privilege to other users or groups through Policies.
Using Service Accounts
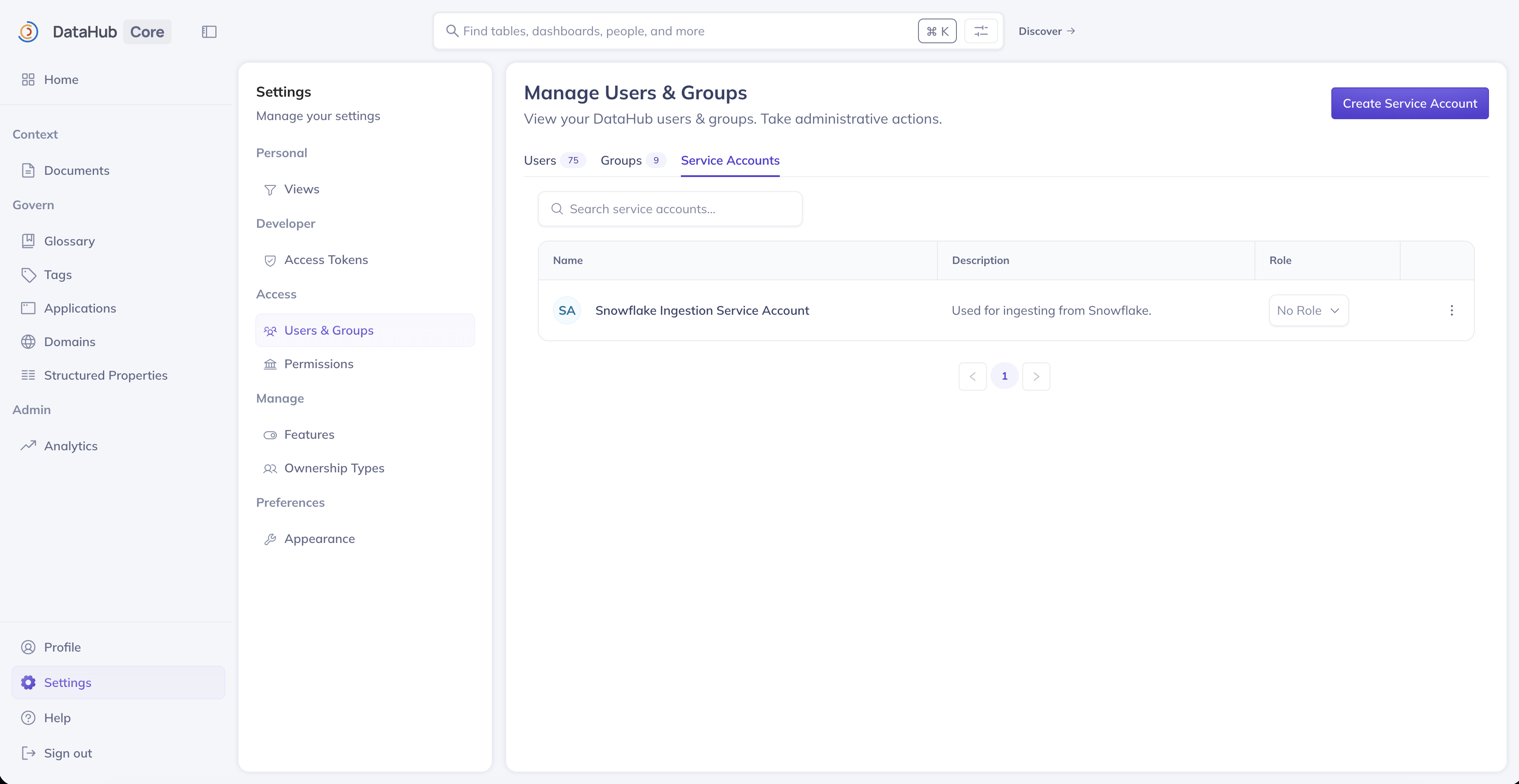
Accessing Service Accounts
Service accounts can be managed from the Settings page in DataHub:
- Navigate to Settings (gear icon in the top navigation)
- Click Users & Groups in the left sidebar
- Select the Service Accounts tab
Creating a Service Account
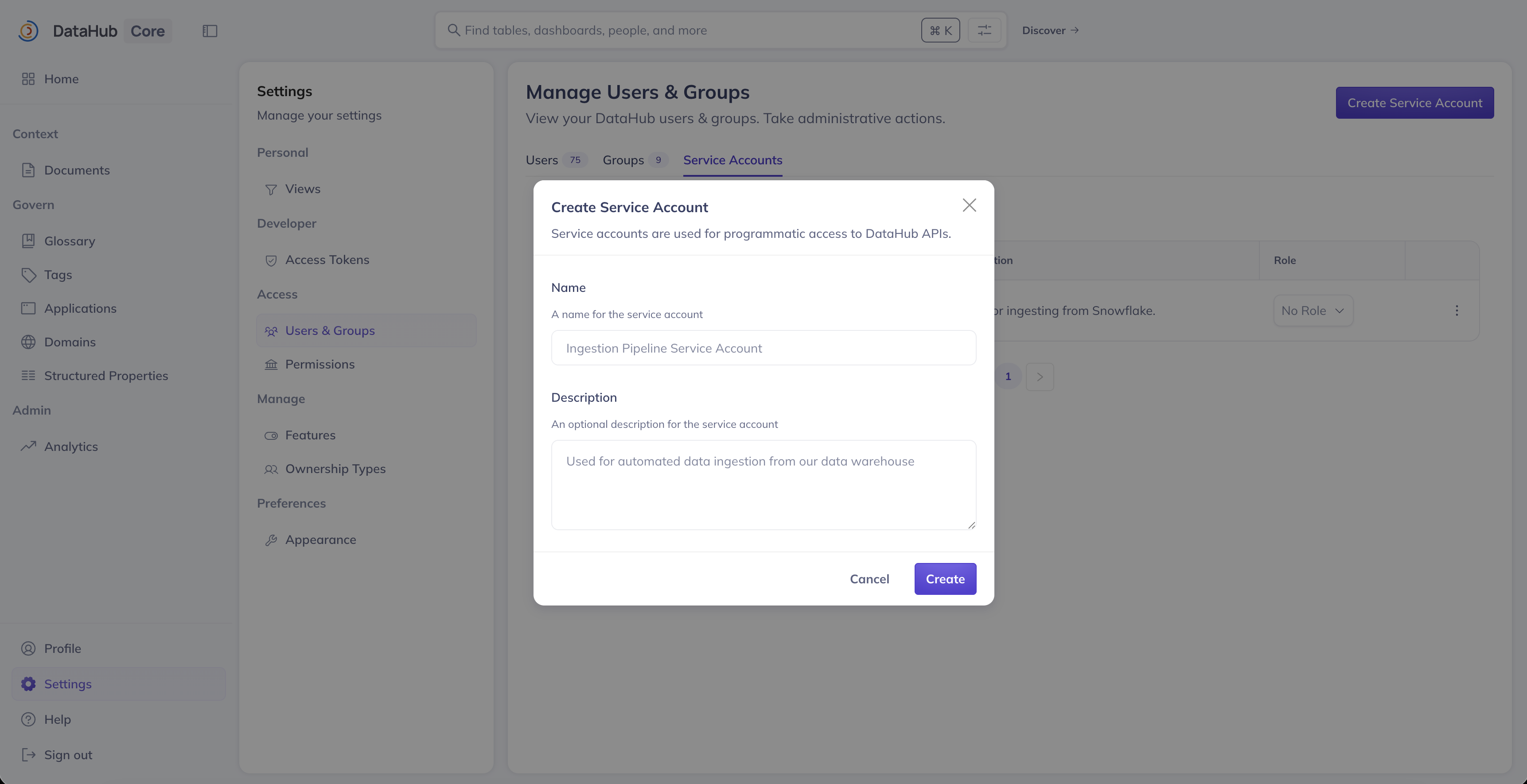
To create a new service account:
- Click the Create Service Account button
- Enter a Name for the service account (e.g., "Ingestion Pipeline", "CI/CD Bot")
- Optionally, add a Description to explain the service account's purpose
- Click Create
The service account will be assigned a unique identifier (URN) automatically. This URN follows the format:
urn:li:corpuser:service_<uuid>
Generating Access Tokens
After creating a service account, you need to generate an access token for it to authenticate with DataHub APIs:
- Navigate to Settings > Access Tokens
- Click Generate new token
- Select Service Account as the token type
- Choose the service account from the dropdown
- Provide a Name for the token (e.g., "production-ingestion-token")
- Select a Duration for the token validity
- Click Generate
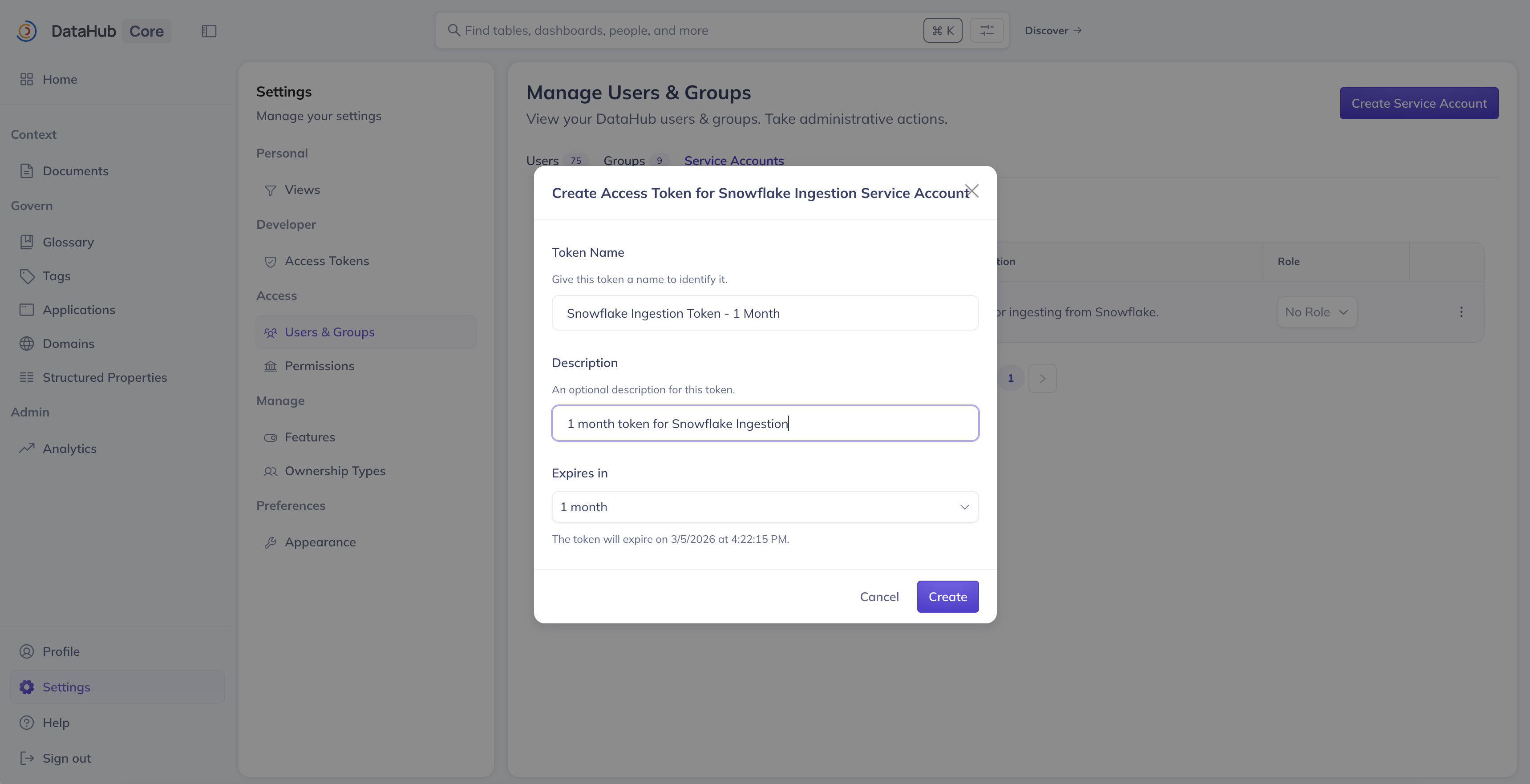
Copy and store the generated token securely. It will only be displayed once and cannot be retrieved later.
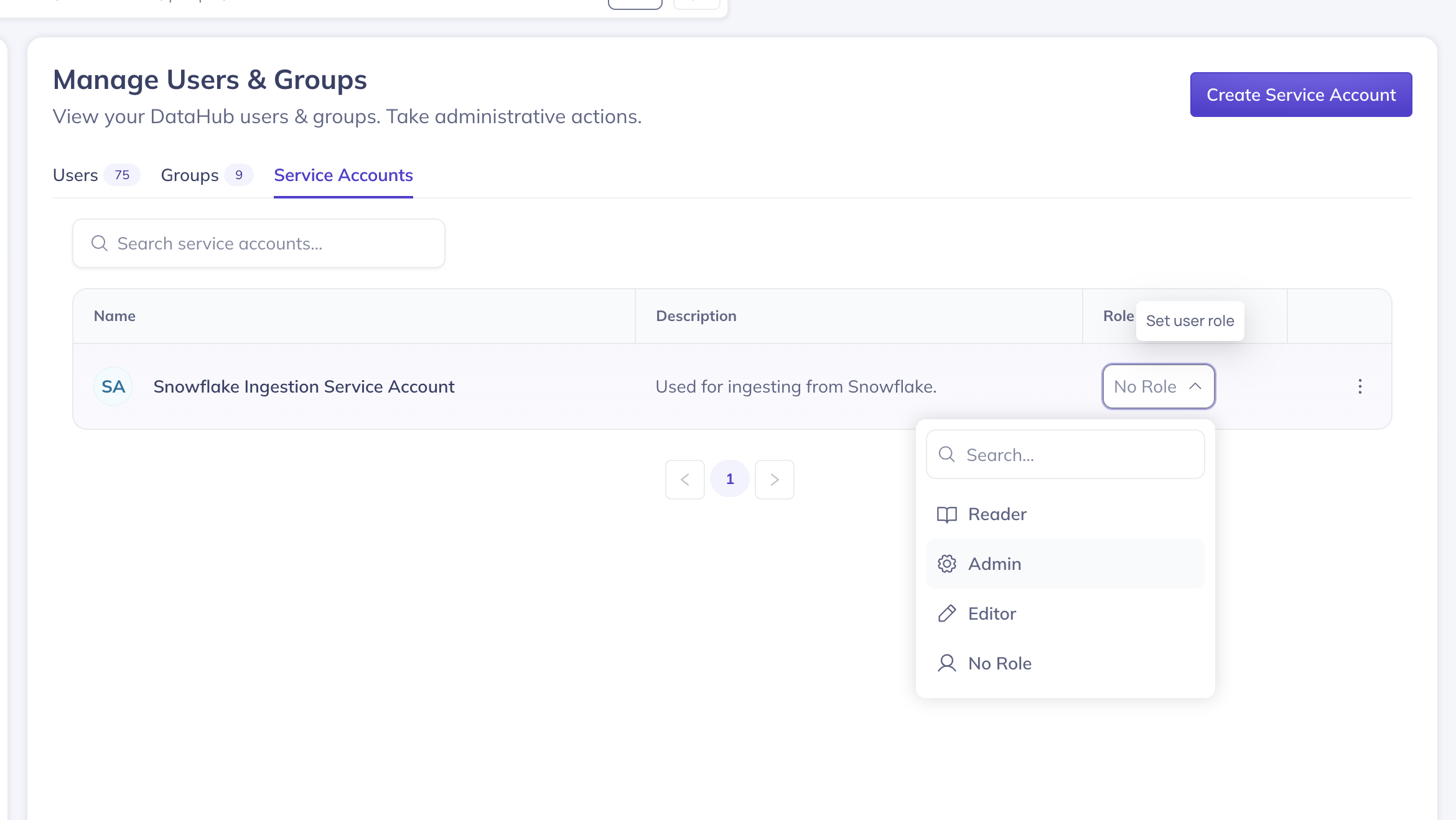
Assigning Roles to Service Accounts
Service accounts can be assigned DataHub roles to control their permissions. To assign a role:
- Navigate to Settings > Users & Groups > Service Accounts
- Find the service account in the list
- Use the Role dropdown to select a role (e.g., Admin, Editor, Reader)
- Confirm the role assignment
Alternatively, you can add service accounts to Policies for more granular permission control.
Deleting a Service Account
To delete a service account:
- Navigate to Settings > Users & Groups > Service Accounts
- Find the service account you want to delete
- Click the 3-dot more menu on the right side
- Click the Delete button (trash icon)
Deleting a service account will immediately invalidate all access tokens associated with it. Any automated workflows using those tokens will stop working.
Revoking Access Tokens
To revoke a specific token without deleting the entire service account:
- Navigate to Settings > Access Tokens
- Find the token you want to revoke
- Click Revoke
- Confirm the revocation
Using Service Account Tokens
Once you have generated an access token for a service account, you can use it to authenticate with DataHub APIs.
With the DataHub CLI
# Set the token as an environment variable
export DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN="<your-service-account-token>"
# Or pass it directly
datahub get --urn "urn:li:dataset:..."
With the Python SDK
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Create an emitter with service account token
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(
gms_server="http://localhost:8080",
token="<your-service-account-token>"
)
# Use the emitter for API calls
emitter.emit(...)
With GraphQL API
curl -X POST 'https://your-datahub-instance/api/graphql' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <your-service-account-token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"query": "{ me { corpUser { urn } } }"}'
With REST API
curl 'https://your-datahub-instance/openapi/v3/entity/dataset/...' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <your-service-account-token>'
GraphQL API Reference
Service accounts can also be managed programmatically using the GraphQL API.
Create a Service Account
mutation createServiceAccount($input: CreateServiceAccountInput!) {
createServiceAccount(input: $input) {
urn
type
name
displayName
description
createdBy
createdAt
}
}
Variables:
{
"input": {
"displayName": "My Ingestion Pipeline",
"description": "Service account for automated data ingestion"
}
}
List Service Accounts
query listServiceAccounts($input: ListServiceAccountsInput!) {
listServiceAccounts(input: $input) {
start
count
total
serviceAccounts {
urn
name
displayName
description
createdBy
createdAt
updatedAt
}
}
}
Variables:
{
"input": {
"start": 0,
"count": 20,
"query": ""
}
}
Get a Service Account
query getServiceAccount($urn: String!) {
getServiceAccount(urn: $urn) {
urn
name
displayName
description
createdBy
createdAt
updatedAt
}
}
Delete a Service Account
mutation deleteServiceAccount($urn: String!) {
deleteServiceAccount(urn: $urn)
}
Create Access Token for Service Account
mutation createAccessToken($input: CreateAccessTokenInput!) {
createAccessToken(input: $input) {
accessToken
metadata {
id
actorUrn
ownerUrn
name
description
}
}
}
Variables:
{
"input": {
"type": "SERVICE_ACCOUNT",
"actorUrn": "urn:li:corpuser:service_<uuid>",
"name": "my-token-name",
"duration": "ONE_YEAR"
}
}
Valid duration options: ONE_HOUR, ONE_DAY, ONE_MONTH, THREE_MONTHS, SIX_MONTHS, ONE_YEAR, NO_EXPIRY
Best Practices
Naming Conventions
Use descriptive names that indicate the purpose of each service account:
ingestion-snowflake-prod- For Snowflake production ingestioncicd-github-actions- For GitHub Actions CI/CD pipelinesairflow-metadata-sync- For Airflow metadata synchronization
Token Rotation
Regularly rotate service account tokens to maintain security:
- Generate a new token for the service account
- Update your automation to use the new token
- Revoke the old token
Least Privilege Access
Assign the minimum permissions required for each service account:
- For ingestion pipelines: Assign a custom policy that only allows creating/updating specific entity types
- For read-only integrations: Use a Reader role or custom read-only policy
- For admin automation: Use the Admin role only when absolutely necessary
FAQ and Troubleshooting
Why can't I see the Service Accounts tab?
The Service Accounts tab is only visible to users with the Manage Service Accounts privilege. Contact your DataHub administrator to request access.
My service account token stopped working
Check the following:
- Token expiration: The token may have expired. Generate a new token.
- Service account deleted: The service account may have been deleted. Create a new one.
- Token revoked: Someone may have revoked the token. Generate a new one.
- Permission changes: The service account's permissions may have been modified.
Can I see which tokens exist for a service account?
Yes, navigate to Settings > Access Tokens and filter by the service account name to see all tokens associated with it. Note that YOU must filter for the owner of the service account to see it. Whoever created the service account will be the token owner.
What happens to a service account's tokens when I delete it?
All tokens associated with a service account are invalidated when the service account is deleted.
Can I use service accounts in policies?
Yes, service accounts can be added to policies just like regular users. Use the service account's URN (e.g., urn:li:corpuser:service_<uuid>) when configuring policy actors.
What's the difference between a personal access token and a service account token?
| Feature | Personal Access Token | Service Account Token |
|---|---|---|
| Associated with | A human user | A service account |
| Permissions | Inherits user's permissions | Based on service account's role/policies |
| Revocation impact | Only affects the token holder | Only affects the specific automation |
| Use case | Individual user API access | Automated workflows and integrations |